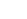
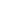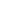Hardware stamping is a fundamental process in manufacturing, used to shape, cut, and form metal components for various industries. From automotive parts to electronics and household items, hardware stamping enables efficient mass production while maintaining precision and consistency. Understanding how this process works reveals why it is essential in modern industrial operations.
1. Material Selection and Preparation
The hardware stamping process begins with careful material selection. Manufacturers choose metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, or copper depending on the final application.
Key Steps in Preparation
- Inspecting metal sheets or coils for thickness and surface quality
- Cleaning and straightening materials to prevent defects
- Cutting large sheets into manageable sizes for stamping machines
Proper preparation ensures that hardware stamping produces components with accurate dimensions and clean edges.
2. Stamping Process and Techniques
Hardware stamping involves pressing a metal sheet into a desired shape using dies and a stamping press. The process can include multiple techniques:
Common Stamping Techniques
- Blanking: Cutting the basic shape out of the sheet metal
- Punching: Creating holes or cutouts in the component
- Bending: Forming the metal into angles or curves
- Embossing: Adding patterns or textures for functional or decorative purposes
A hardware stamping operation may combine several techniques in a single production cycle to meet design specifications efficiently.
3. Tooling and Die Design
- The precision of hardware stamping relies heavily on the quality of tooling and dies.
- Dies are designed to exact dimensions to minimize waste
- Tool materials are chosen to withstand repeated high-pressure impacts
- Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance and prevents misalignment
- Well-designed tooling allows for accurate, repeatable results and reduces the risk of material defects.
4. Automation and Production Efficiency
- Modern hardware stamping incorporates automation to enhance speed and consistency.
- Automated feeders supply metal sheets to presses without manual handling
- Robotic arms remove finished parts, reducing labor costs
- Sensors monitor stamping force and alignment to prevent errors
These automation strategies improve productivity while maintaining consistent quality across large production runs.
5. Quality Control and Inspection
After stamping, components undergo quality checks to ensure they meet specifications.
Dimensional measurement using calipers or coordinate measuring machines
Surface inspections to detect scratches, burrs, or deformities
Functional tests for components with moving parts or assembly requirements
Quality control ensures that every hardware stamping output is suitable for its intended use.
6. Applications and Versatility
Hardware stamping is versatile and used in a wide range of industries:
- Automotive: brackets, clips, and body panels
- Electronics: connectors, terminals, and housings
- Furniture: fasteners, hinges, and decorative trims
- Appliances and tools: switches, panels, and structural parts
Its flexibility and precision make hardware stamping indispensable for mass production across sectors.
7. Cost and Sustainability Considerations
- Hardware stamping can be an efficient, cost-effective manufacturing method.
- High-speed production reduces labor and time per part
- Material waste is minimized through precise die design
- Some factories recycle scrap metal, contributing to sustainability
This combination of efficiency, precision, and environmental consideration makes hardware stamping a preferred method for many manufacturers.
Hardware stamping remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling industries to produce high-quality metal components efficiently. Through careful material selection, precision tooling, automation, and rigorous quality control, stamped hardware meets the diverse needs of automotive, electronics, furniture, and appliance sectors. Understanding the processes behind hardware stamping highlights its importance in producing consistent, reliable, and cost-effective components.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体